Life Cycle Of a Frog Lesson
Use this life cycle of a frog lesson and printable pack to learn more about frogs and nature. Then, head outside to find a few frogs or raise tadpoles on your own!
As I’m writing this, I can hear frogs singing in a small pool of water created each year by spring rains. The warm weather has awakened the frogs from their dormancy, and they are out looking for food and mates. It’s an ideal time to do a hands-on study of the life cycle of a frog and learn how they breathe, protect themselves, and much more.
Pools of water are perfect for frogs, or toads, to lay their eggs. The water is still so the eggs won’t be disturbed and there are no fish to eat the eggs.
Related post: Spring Toads (with a video of toads singing in a small pond)
The life cycle of a frog begins with the laying of the eggs. A life cycle is all the changes an organism goes through during it’s lifetime. All organisms have a life cycle and go through changes. Humans start as babies then continue to grow into children then adolescents then adults. Other mammals go through a similar life cycle.
What makes the life cycle of a frog extraordinary is that while the babies of most organisms are just smaller versions of adults, frog babies don’t look like frogs at all. Instead of simply growing larger, frogs go through a process called metamorphosis. Metamorphosis is a huge developmental change in the form or structure of an animal. Let’s walk through the stages of a frog’s life cycle and you will see what I mean.
A Little Background About Frogs
Before we look at the life cycle of a frog, here are a few facts about frogs.
- Frogs are amphibians, which means they spend part of their lives in water and part of their lives on land. Toads, salamanders, newts, and caecilians are also amphibians. Amphibians typically start their lives in water as larvae or tadpoles, which breathe through gills and have tails for swimming. As a side note, the word amphibian
- As they mature, frogs develop lungs for breathing air and legs for moving on land.
- Since their skin is thin and permeable, it can easily dry out. So, it’s important amphibians live in a wet environment where they can keep their skin moister.
- Frogs are able to absorb water and oxygen through their skin.
- Frogs are found all over the world, except for Antarctica. They can live in a variety of habitats, including forests, deserts, and even in urban areas.
- Frogs are carnivorous and feed on insects, spiders, and other small animals. They catch their prey using their sticky, retractable tongue.
- Some species of frogs can change color to match their surroundings, which helps them to blend in and avoid predators.
- Male frogs often make loud calls to attract females during the breeding season. Some species of frogs can be heard up to a mile away.
- Many species of frogs hibernate during the winter to survive the cold temperatures.
- The largest species of frog is the Goliath frog (Conraua goliath), which can weigh up to 7.2 pounds (3.3 kilograms) and measure over a foot (30 centimeters) long.
- Some species of frogs can jump up to 20 times their own body length in a single leap.
- Some frogs can survive for long periods of time without food or water by slowing down their metabolism and entering a state of torpor.
Life Cycle Of A Frog
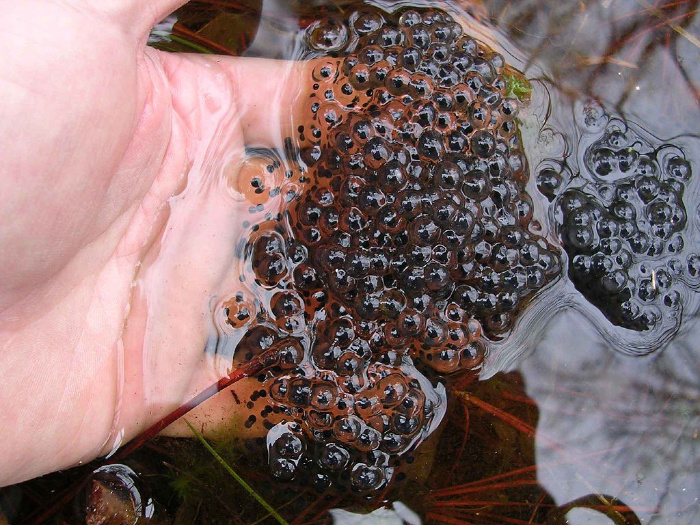

Life Cycle of a Frog – Stage 1 – Eggs of Frogspawn
Female frogs will lay hundreds of eggs at a time in a large mass usually in still, stagnant water. She does this to protect the eggs from being washed away and to protect them from predators.
Until these eggs are fertilized, the eggs are referred to as frogspawn is a term used to describe the eggs laid by female frogs, toads, and some other amphibians. The eggs are usually laid in a jelly-like mass, which is called a “spawn.” The spawn can be found in ponds, streams, or other bodies of water where the amphibians live and breed.
Frogspawn typically consists of many small, black eggs that are surrounded by a clear, jelly-like substance. As the eggs develop, they expand and absorb water from the surrounding environment, causing the jelly to become larger and more transparent.
Life Cycle of a Frog – Stage 2 – Embryos
Males will then fertilize the eggs in the water. The fertilized eggs are referred to as embryos.
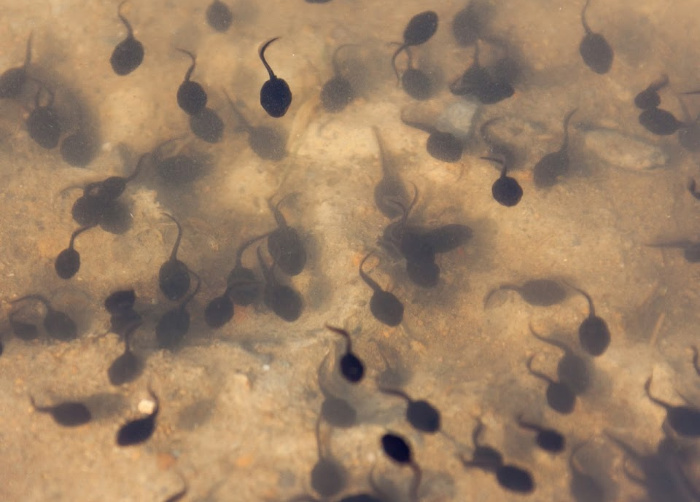

Life Cycle of a Frog – Stage 3- Tadpole
Depending upon the species of frog, the egg stage will last 6-21 days until they hatch into tadpoles. Tadpoles look more like fish than frogs with their long tails, gills, and lack of legs. Tadpoles live in the water breathing through their gills and feeding on algae and other small organisms in the water. Tadpoles have a tail and no legs at this stage.
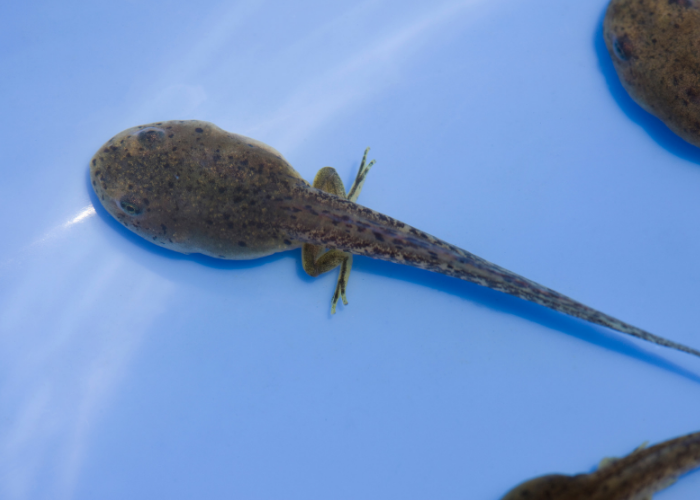

Life Cycle of a Frog – Stage 4- Metamorphosis into a Late Tadpole
Over the next few weeks of life, the tadpole starts to undergo metamorphosis. Skin starts to grow over the gills as lungs start to develop. Hind legs, also develop and the head starts to become distinct. They lose their tail. Their diet changes its diet from vegetarian to carnivorous. At this stage we call them a froglet.
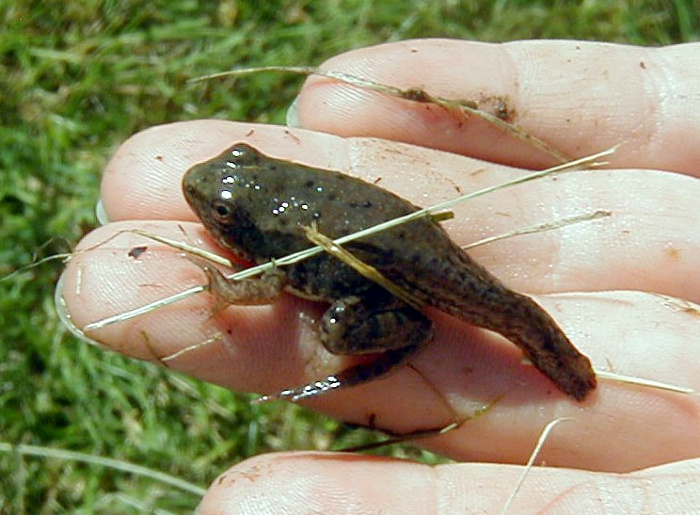

Life Cycle of a Frog – Stage 5 – Young Frog or Froglet
By about 9 weeks, the frog grows front legs. It now looks more like a frog than a tadpole. The froglet still has a tail that is full of nutrients. he froglet is still small and has a slimy skin, but it has fully developed legs and lungs, and can breathe both in air and in water. As the froglet matures, it uses up those nutrients and the tail gets shorter and shorter. The shorter tail and 4 legs mean it can now hop on land.
Once metamorphosis is complete, the tadpole has become a young frog, also known as a froglet. The young frog is still small and has a slimy skin, but it has fully developed legs and lungs, and can breathe both in air and in water.
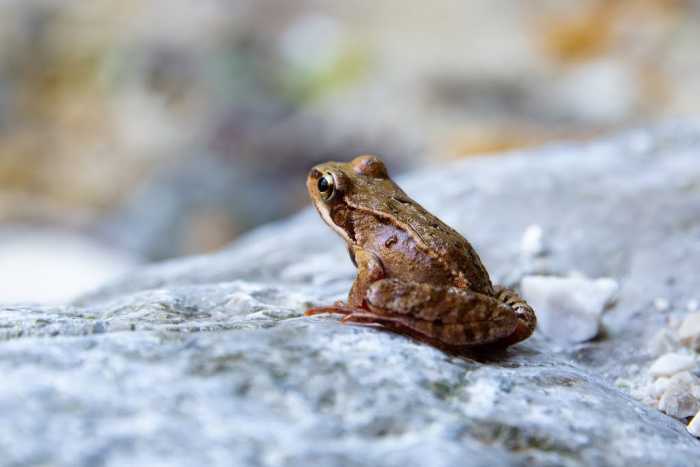

Life Cycle of a Frog – Stage 6 – Adult Frog
At about 12-16 weeks (depending upon the species and this is just an average), the tail disappears, and the frog is now an adult and can start the life cycle over again. Adult frogs can live on land or in water, and their diet typically consists of insects and other small animals.
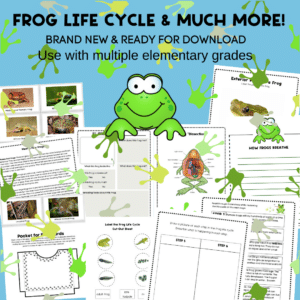
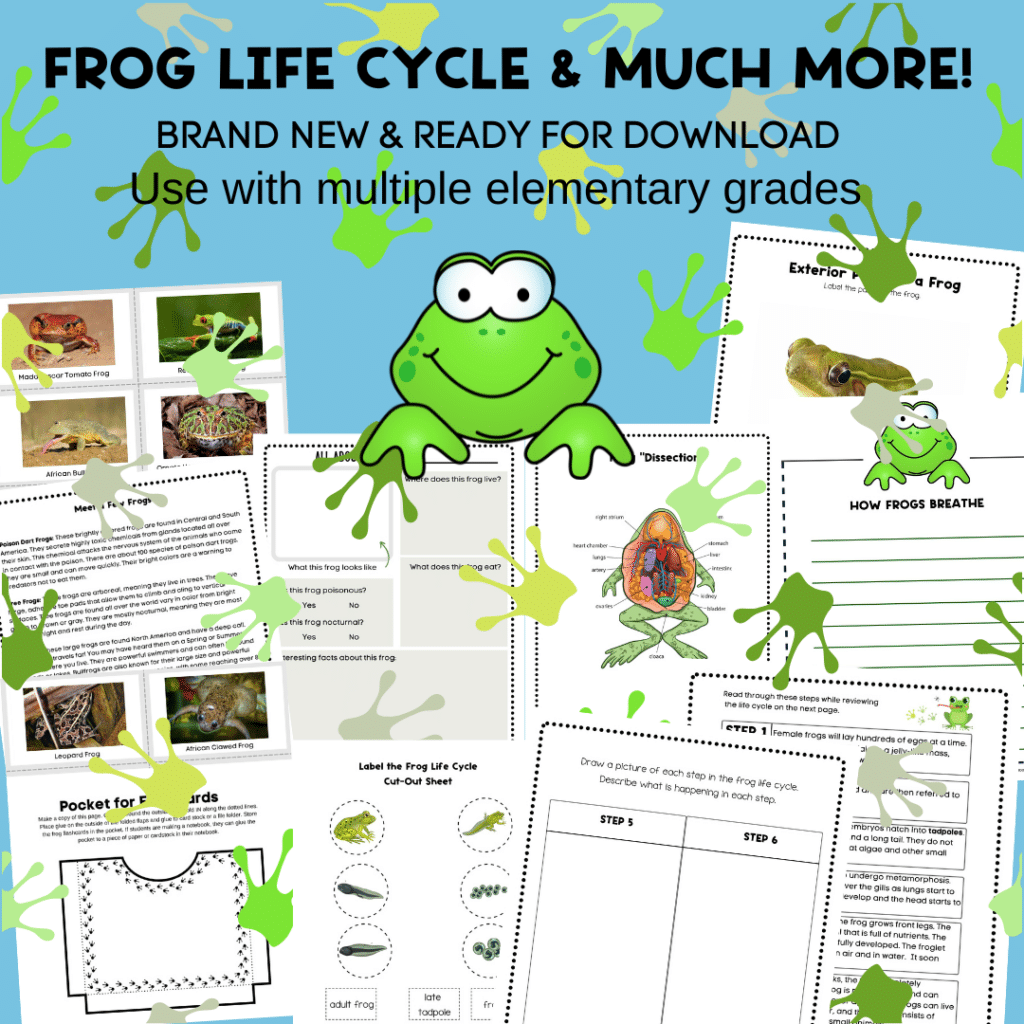
Life Cycle Of A Frog Printable
Use this life cycle of a frog printable pack to reinforce the above lesson. Includes anatomy, how frogs protect themselves, how frogs breathe, flashcards for 10 different frogs, report forms, puzzles, coloring pages just for fun.
Want to learn more about frogs and do a fun frog activity?? Don’t miss the end of the post!!
More Frog Information and Activities
We’ve done some fun frog studies over the years. Here are a few posts packed with info, links, and fun that you will want to check out!
If you have students in grades 8-12 and are doing some higher level animal biology, you might want to check out these free ebooks from the Amphibian Survival Alliance.
Herpmapper is an organization that tracks amphibian and reptile sightings across the world. Citizens can log in and record a sighting. This data is shared with scientists who are conducting research, leading preservation activities, or planning conservation efforts. Plus, it’s fun to see what has been spotted in your area of the country.
How to Tell the Difference Between Frog and Toad Spawn from Wildfowl & Wetlands Trust Limited in the UK.
What Makes The Frog’s Tongue So Cool? {plus a frog tongue craft!}
Can The Endangered Dusky Gopher Frog Be Saved?
I hold a master’s degree in child development and early education and am working on a post-baccalaureate in biology. I spent 15 years working for a biotechnology company developing IT systems in DNA testing laboratories across the US. I taught K4 in a private school, homeschooled my children, and have taught on the mission field in southern Asia. For 4 years, I served on our state’s FIRST Lego League tournament Board and served as the Judging Director. I own thehomeschoolscientist and also write a regular science column for Homeschooling Today Magazine. You’ll also find my writings on the CTCMath blog. Through this site, I have authored over 50 math and science resources.